Carotid Angioplasty
Carotid Angioplasty: Minimally Invasive Treatment for Carotid Artery Disease
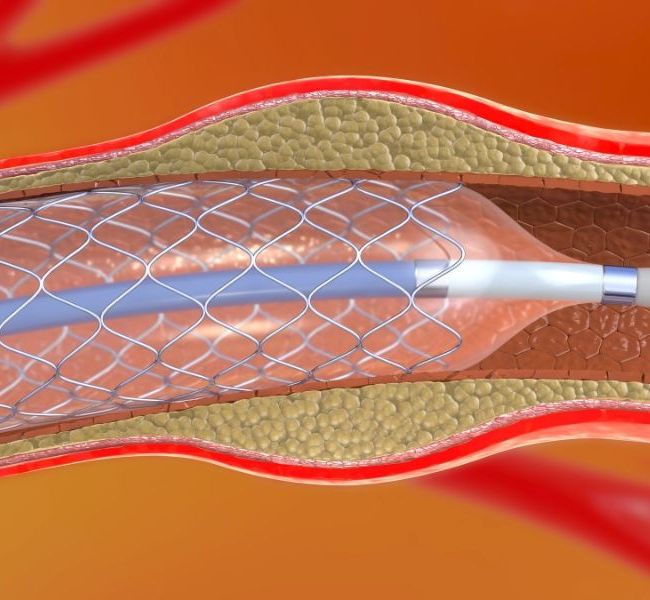
Carotid Angioplasty
Carotid angioplasty is a minimally invasive procedure aimed at treating carotid artery stenosis, a condition that increases the risk of stroke. It involves widening the narrowed artery using a balloon-tipped catheter.
Through careful catheter insertion and balloon inflation, plaque is compressed against the arterial walls, restoring blood flow to the brain. This intervention reduces the risk of stroke and transient ischemic attacks (TIAs), offering a less invasive alternative to traditional surgical approaches for managing carotid artery disease.
Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how Carotid Angioplasty typically works
Patients undergo a thorough assessment, including medical history review and diagnostic imaging (e.g., carotid ultrasound, CT angiography), to determine the severity and location of carotid artery stenosis.
Anesthesia or conscious sedation is administered to ensure patient comfort and relaxation during the procedure.
Gain access to the carotid artery by inserting a catheter, typically through the femoral artery in the groin, and navigating it to the target site under fluoroscopic guidance.
Thread a guidewire through the catheter and advance it beyond the stenotic lesion in the carotid artery to facilitate balloon placement.
Inflate a balloon-tipped catheter at the site of stenosis to compress the plaque against the arterial walls, widening the narrowed carotid artery and restoring blood flow to the brain.
Inject contrast dye through the catheter and perform angiography to visualize the carotid artery, assessing the extent of stenosis before and after balloon inflation.
In some cases, a stent may be deployed to provide structural support and maintain the patency of the carotid artery following angioplasty.
Patients are monitored in a recovery area for any immediate complications, such as bleeding or changes in blood pressure, before being discharged with instructions for post-procedural care. Follow-up appointments are scheduled to monitor the patient’s progress and assess the long-term effectiveness of the procedure.
Carotid Angioplasty is used in various medical specialties
Carotid angioplasty finds utility in several medical disciplines, including interventional radiology, neurology, vascular surgery, and cardiology. These specialties collaborate to diagnose and manage carotid artery stenosis, a condition characterized by narrowing of the carotid arteries supplying blood to the brain, which can lead to strokes or transient ischemic attacks (TIAs).
Leading cardiologist, dedicated to pioneering treatments, enhancing heart health, and transforming lives through compassionate care.
About Us
Contact Info
- +91-8928 273 010
- drameyatirodkar@gmail.com
- 302, Third Floor Neminath Square, S M Diagnostics S V Road off Ram Mandir signal Goregaon West 400104
Copyright @2024. All Right Reserved | Designed By Rebecca Digital.

