Color Doppler Echocardiography
Color Doppler echocardiography visualizes blood flow within the heart.
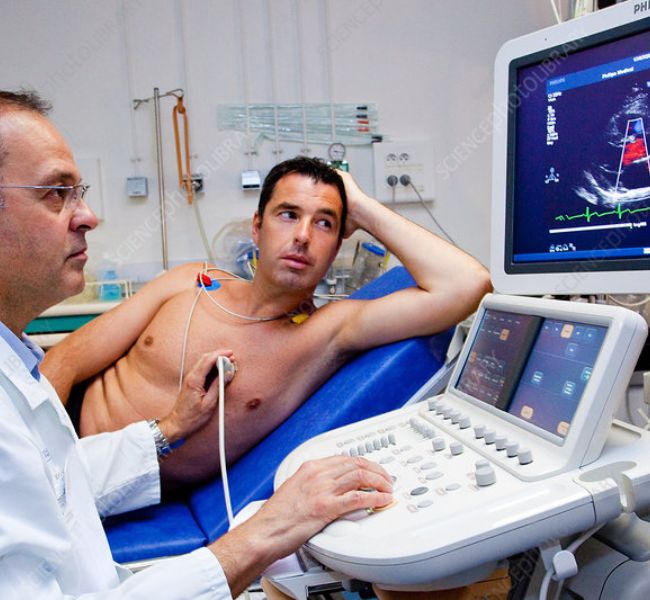
Color Doppler Echocardiography
Color Doppler echocardiography is an advanced ultrasound technique that uses color coding to visualize blood flow within the heart. By highlighting the direction and speed of blood flow, it provides detailed images of heart structures and their function, helping to diagnose conditions like valve disorders and congenital defects.
During the procedure, a transducer is placed on the chest to emit sound waves that reflect off heart structures and moving blood. The reflected waves are translated into color-coded images, allowing doctors to assess issues such as valve regurgitation and abnormal blood flow patterns, making it a crucial tool for accurate cardiac evaluation and management.
Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how Color Doppler Echocardiography typically works:
The patient lies on an examination table, usually on their left side, to optimize heart imaging. Electrodes may be placed on the chest to monitor heart activity.
A gel is applied to the chest to help the ultrasound transducer, a small handheld device, make good contact with the skin. The transducer emits and receives sound waves.
The technician moves the transducer over the chest to capture images of the heart. The device uses sound waves to create detailed images of the heart’s structures and blood flow.
The Color Doppler feature analyzes how sound waves are altered by moving blood cells. It translates these changes into color-coded images showing the direction and speed of blood flow within the heart and vessels.
The color-coded images are reviewed in real-time to assess blood flow patterns, heart valve function, and the presence of any abnormalities such as regurgitation or stenosis.
The images and data are interpreted by a cardiologist or healthcare provider to diagnose conditions, guide treatment, and monitor heart health.
After the procedure, the gel is cleaned off, and the patient can resume normal activities. The results are discussed with the patient, and follow-up steps are planned if necessary.
The images and findings are documented and compiled into a detailed report by the technician or cardiologist. This report is then reviewed with the patient, and any necessary follow-up or treatment plans are discussed based on the results.
Color Doppler echocardiography is commonly used across various medical specialties
Coronary angiography is primarily used in the diagnosis and assessment of coronary artery disease (CAD), which is the most common type of heart disease. CAD occurs when the coronary arteries, which supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle, become narrowed or blocked due to the buildup of plaque (atherosclerosis). This can lead to symptoms such as chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, or even heart attack.
Leading cardiologist, dedicated to pioneering treatments, enhancing heart health, and transforming lives through compassionate care.
About Us
Contact Info
- +91-8928 273 010
- drameyatirodkar@gmail.com
- 302, Third Floor Neminath Square, S M Diagnostics S V Road off Ram Mandir signal Goregaon West 400104
Copyright @2024. All Right Reserved | Designed By Rebecca Digital.

