A healthcare provider reviews the results to diagnose respiratory conditions, evaluate their severity, and determine the appropriate treatment or management plan.
Spirometry
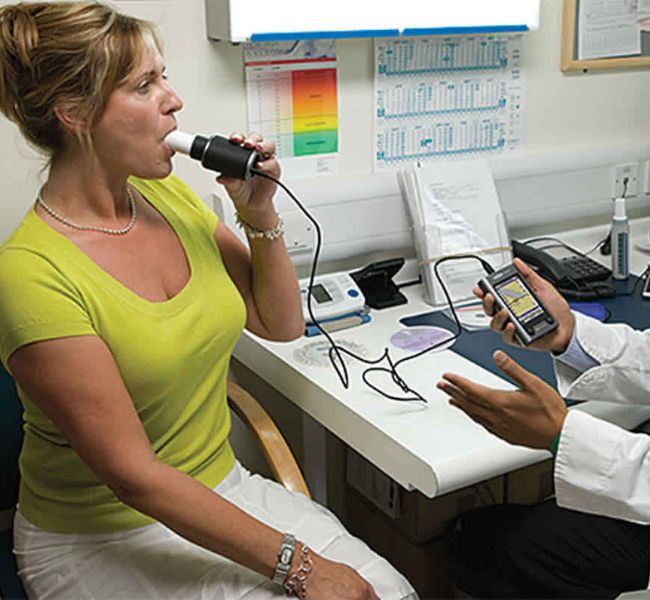
Spirometry is a diagnostic test used to measure lung function by assessing breathing capacity. It involves the patient inhaling deeply and then exhaling into a device called a spirometer, which records the volume and speed of air expelled from the lungs. This test helps evaluate respiratory conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and other disorders that affect breathing.
The results from spirometry provide valuable information about lung health, including how well the lungs are working and whether there are any obstructions or restrictions in airflow.
Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how spirometry typically works
The patient is instructed to sit upright and may be asked to avoid eating a large meal or using bronchodilators before the test. The spirometer and necessary equipment are set up by the technician.
The patient wears a nose clip to ensure all breath goes through the mouth and is seated comfortably. A disposable mouthpiece is attached to the spirometer.
The patient takes a deep, full breath in, expanding their lungs as much as possible.
The patient exhales forcefully and completely into the mouthpiece. This is done rapidly and as hard as possible to measure the maximal airflow and volume.
The spirometer records the volume and speed of air expelled during exhalation, generating data on metrics like Forced Vital Capacity (FVC) and Forced Expiratory Volume in one second (FEV1).
he test may be repeated several times to ensure accurate and consistent results.
The collected data is analyzed to assess lung function, identify any airflow limitations or obstructions, and compare the results to normal values or previous tests.
Spirometry is commonly used across various medical specialties to assess and monitor lung function
Spirometry is widely used across various medical specialties to assess and monitor lung function. Pulmonologists rely on it to diagnose and manage conditions like asthma and COPD, while internists use it to evaluate unexplained respiratory symptoms. Cardiologists may use spirometry to understand the effects of cardiovascular conditions on the lungs, and allergists monitor asthma and other allergic respiratory issues. Additionally, occupational medicine specialists use it to track lung health in workers exposed to respiratory hazards. This versatile tool helps provide critical insights into respiratory health across multiple fields.
Leading cardiologist, dedicated to pioneering treatments, enhancing heart health, and transforming lives through compassionate care.
About Us
Contact Info
- +91-8928 273 010
- drameyatirodkar@gmail.com
- 302, Third Floor Neminath Square, S M Diagnostics S V Road off Ram Mandir signal Goregaon West 400104
Copyright @2024. All Right Reserved | Designed By Rebecca Digital.

